What is schema markup?
Schema markup is code that enables search engines to understand and categorize web page content. Google uses schema markup to show rich results, which are more engaging for searchers than regular search results.
If you want your pages to have a prominent and eye-catching spot in relevant search engine results pages (SERPs), you need to implement schema markup or structured data on them.
Need help getting started on schema markup? Let this article be your guide as it answers these questions:
- What is schema markup?
- Why is schema markup important for SEO?
- What are the different types of schema markup?
- How do you add schema markup for your pages?
- What are schema markup best practices?
What is schema markup?
Schema markup is code that enables search engines to understand and categorize web page content. Google uses schema markup to show rich results, which are more engaging for searchers than regular search results.
Why is schema markup important for search engine optimization (SEO)?
Schema markup is important for SEO because using it provides benefits for both search engines and users.
Structured data gives search engines explicit instructions about your pages’ content. As a result, it helps search engines understand and index your pages better. As shown in the example below, Google also uses schema markup to display your page as a rich result in SERPs.
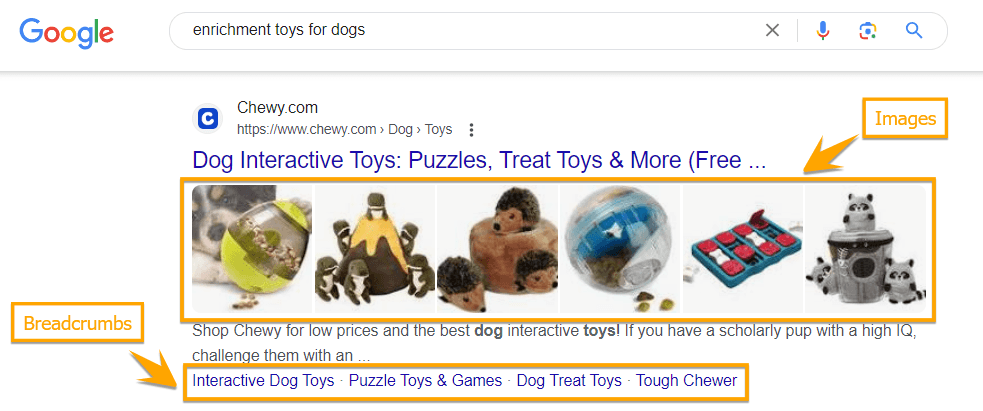
Schema markup also makes the search experience more engaging among users, thus increasing your click-through rates. Structured data provides searchers with more details about your page, giving them a clue about what to expect when they click on your page.
Types of schema markup
Google can understand 30 types of schema markup for various types of websites. We’re not going to include all of those on this page, but here are some of the most common ones you’ll find in SERPs:
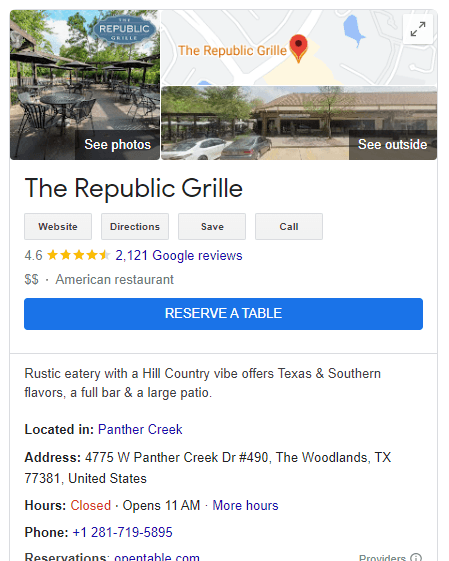
Local business
The local business rich result shows up in the Google knowledge panel, displaying a local service business’s details such as:
- Address
- Business hours
- Phone numbers
- Link to make a reservation or book an appointment
- Ratings
- Reviews
- Information provided by the local business
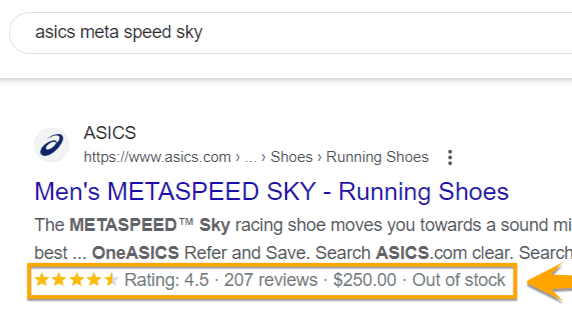
Product
This schema markup for ecommerce websites provides information about a product, including price, availability, and review ratings.
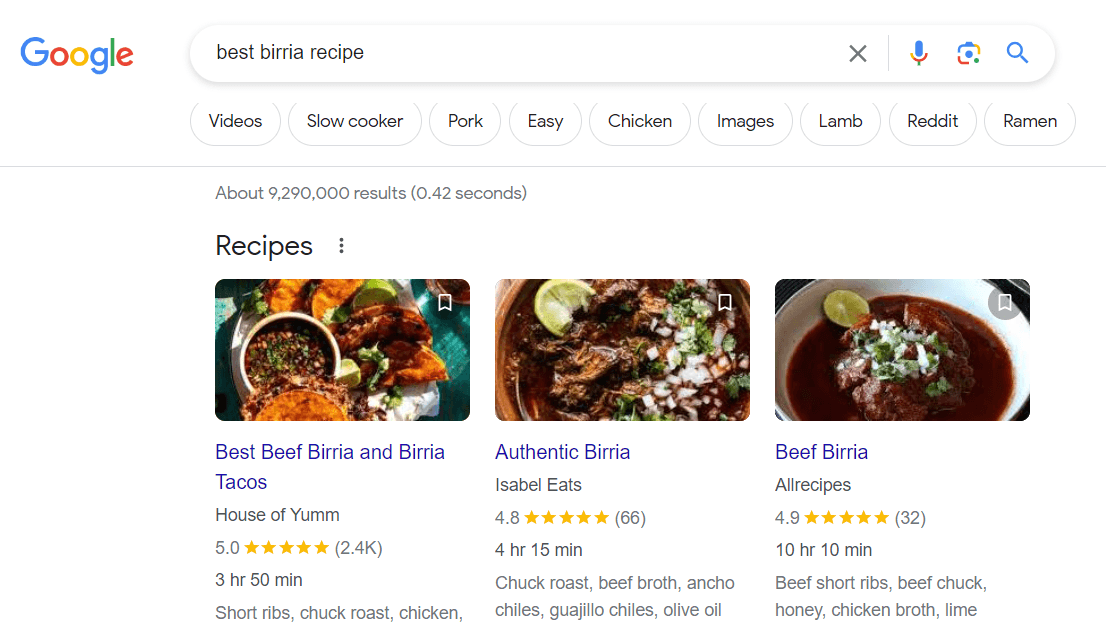
Recipe
The recipe markup can be shown as an individual rich result or part of a carousel. This markup can appear in SERPs and image results.
How to add schema markup for your pages
Here’s your step-by-step guide to generating schema markup for your pages:
- Visit Google’s Structured Data Markup Helper
- Select a page from your site that you’ll mark up
- Mark up the different elements on your page
- Generate the HTML code
- Add your schema markup code to your site
- Test your schema markup
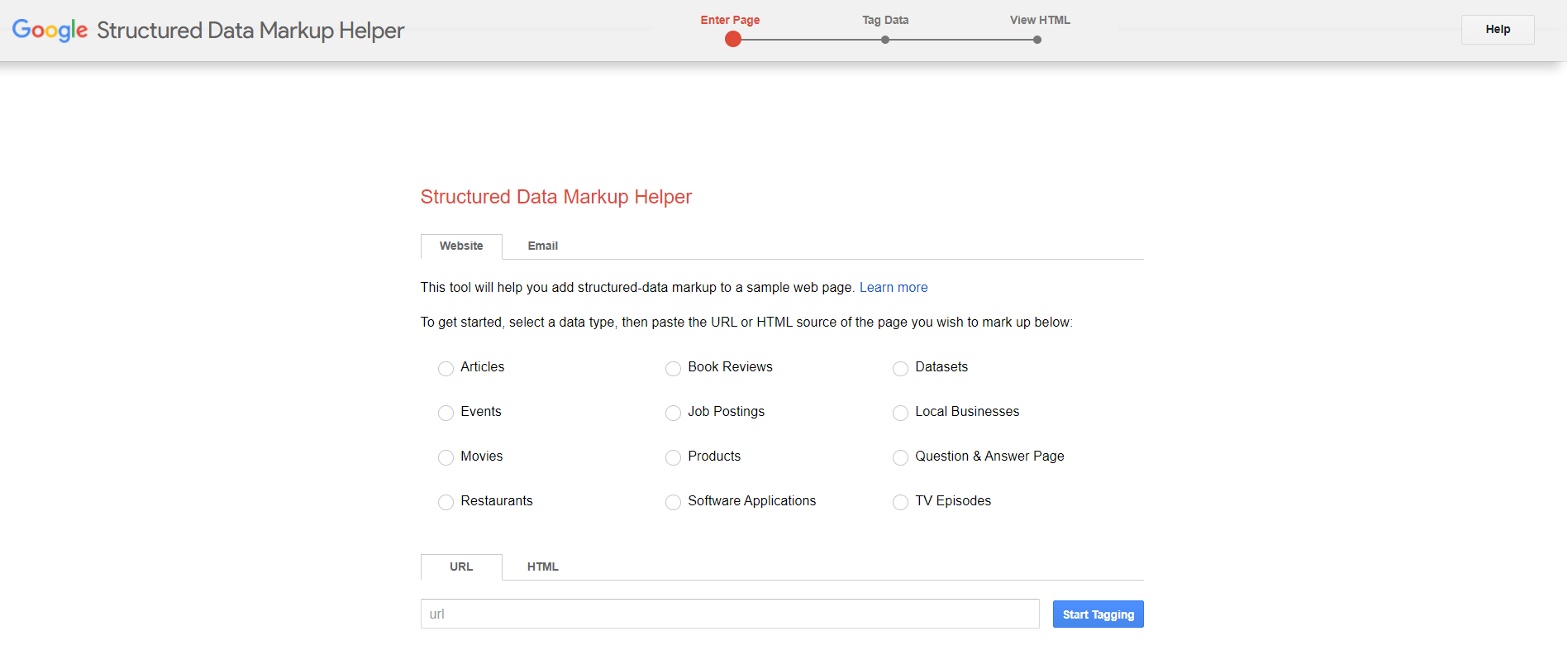
1. Visit Google’s Structured Data Markup Helper
The Structured Data Markup Helper is a tool that helps you create markup elements on your page.
2. Select a page from your site that you’ll mark up
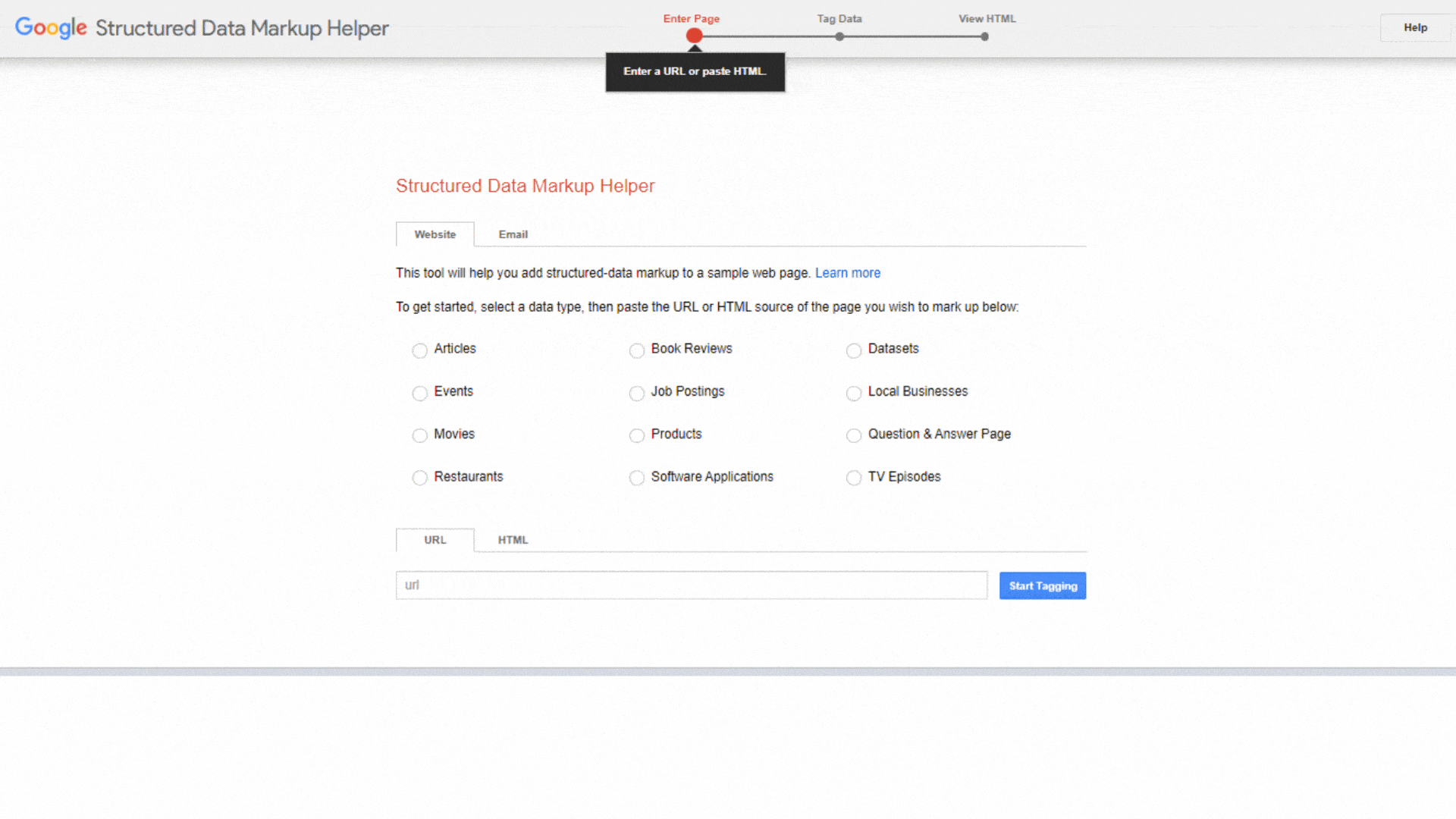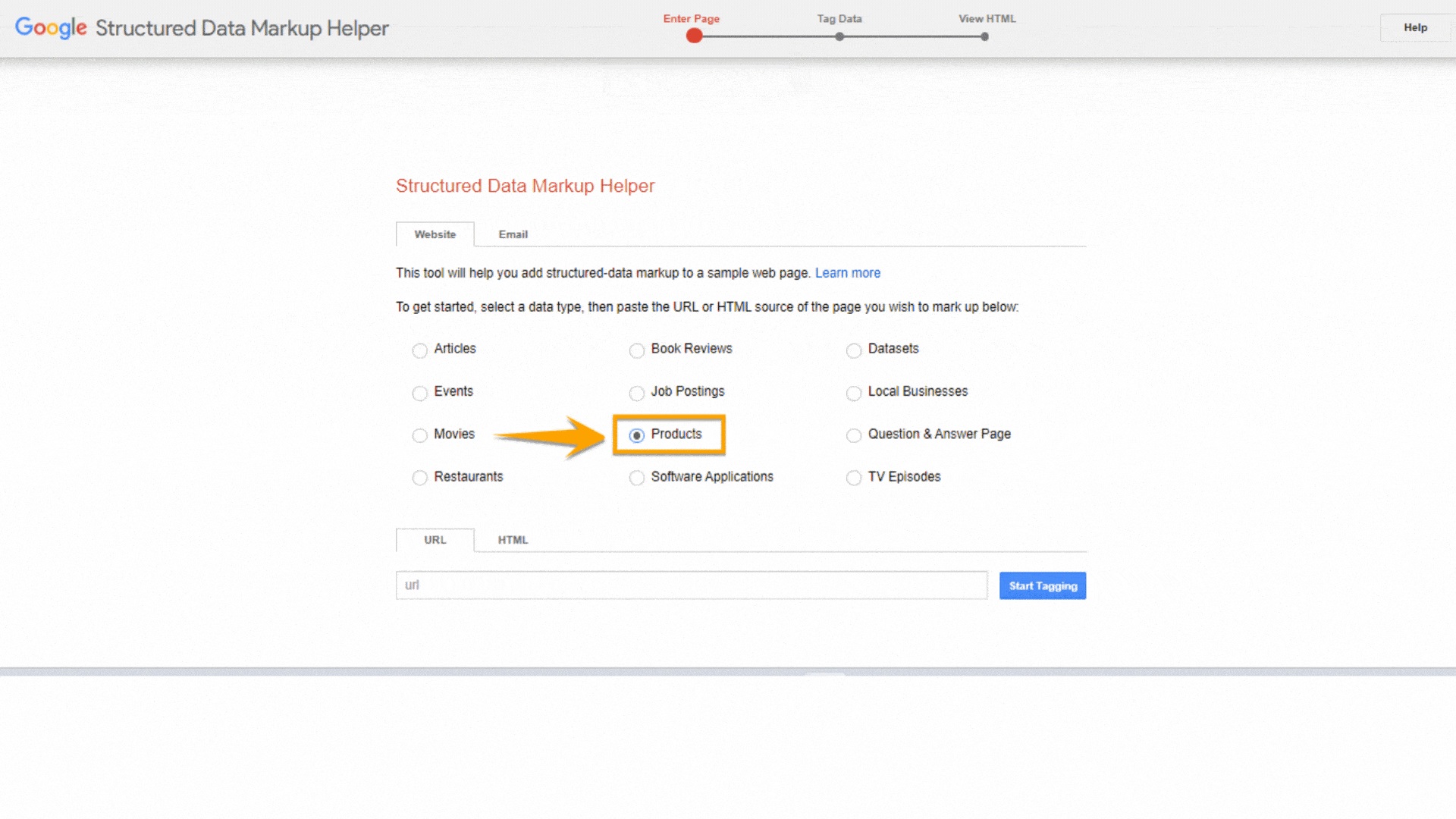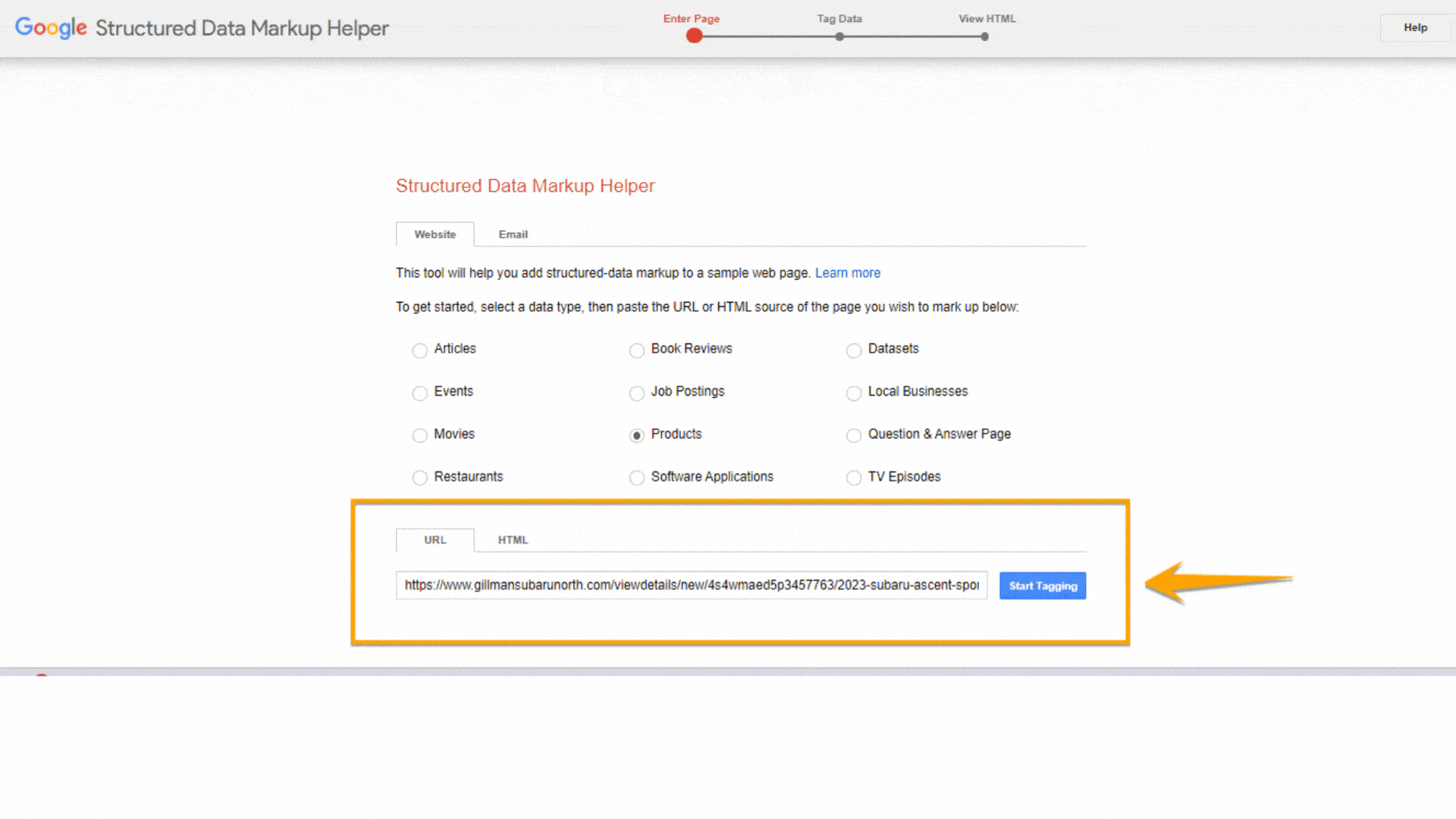
Once you’ve selected a page on your site, tick the radio button of the appropriate data type that you’ll mark on the page on the Structured Data Markup Helper. In our example, we chose the Product markup for a product page.
Then, paste either the page’s URL you want to mark up or your HTML code.
3. Mark up the different elements on your page
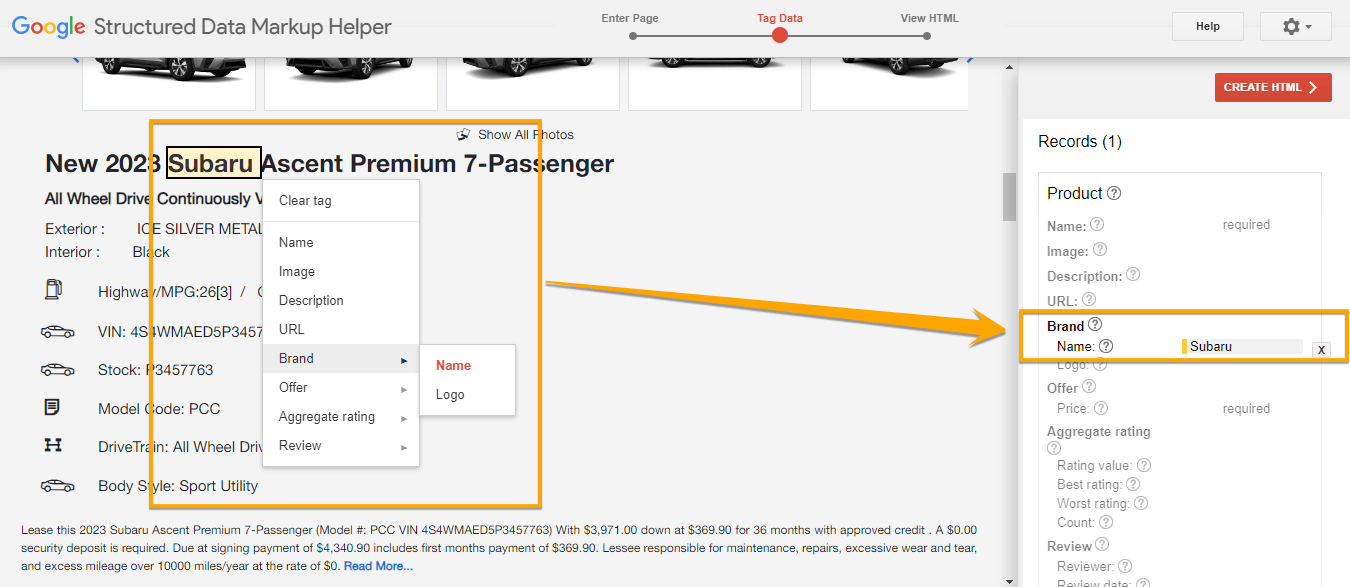
If you add your URL, you can start marking up your page by selecting text or images. In the example below, the brand name of the product is selected. On the right side, your recorded tags will appear.
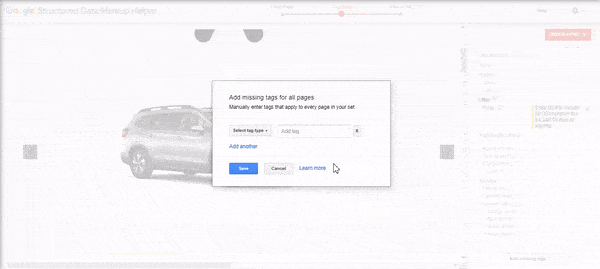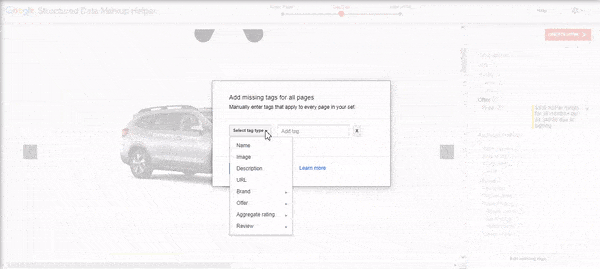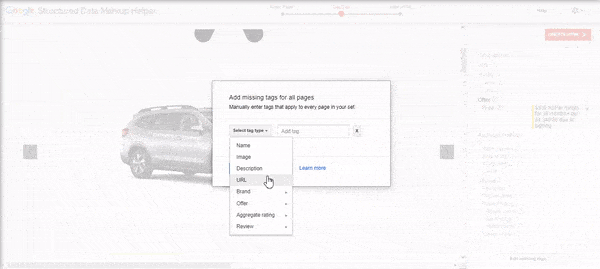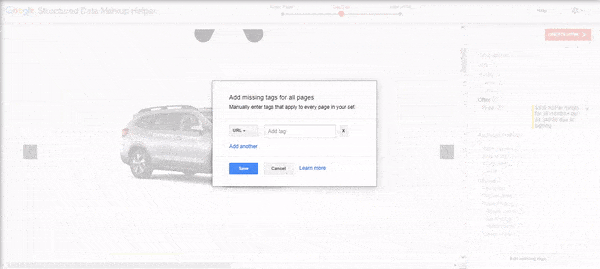
Want to add other tags? You can click the Add Missing Tags button in the lower right-hand corner to add tags manually.
While a structured data best practice is to add tags only found on the page, you can still add tags like the page URL.
4. Generate the HTML code
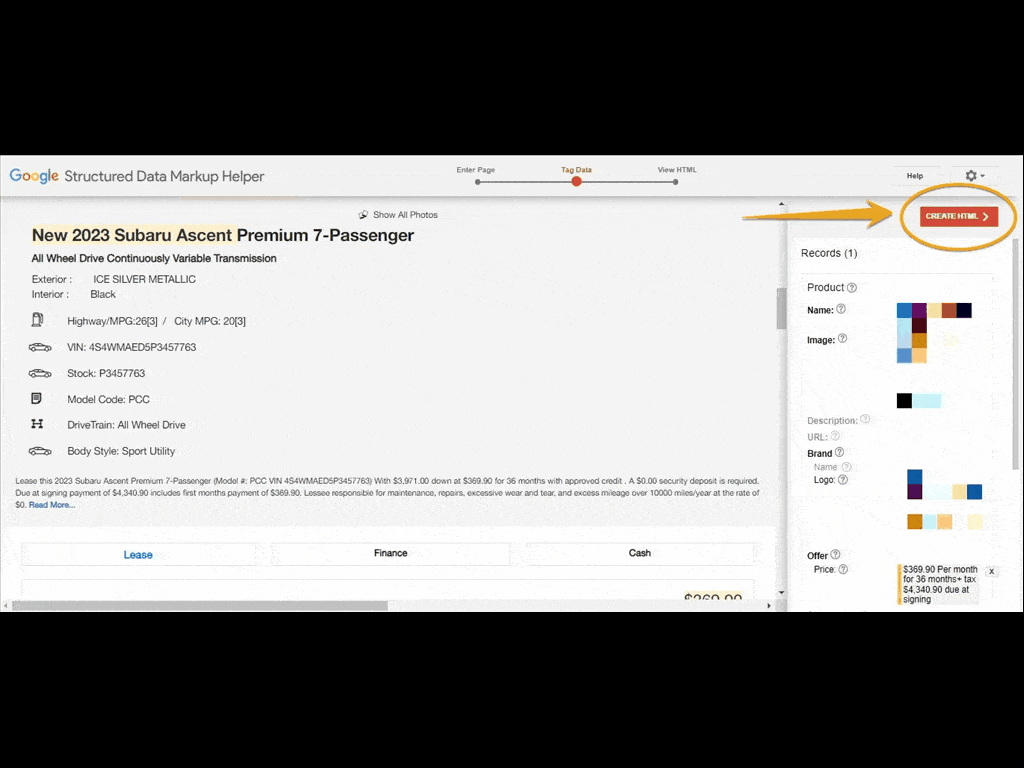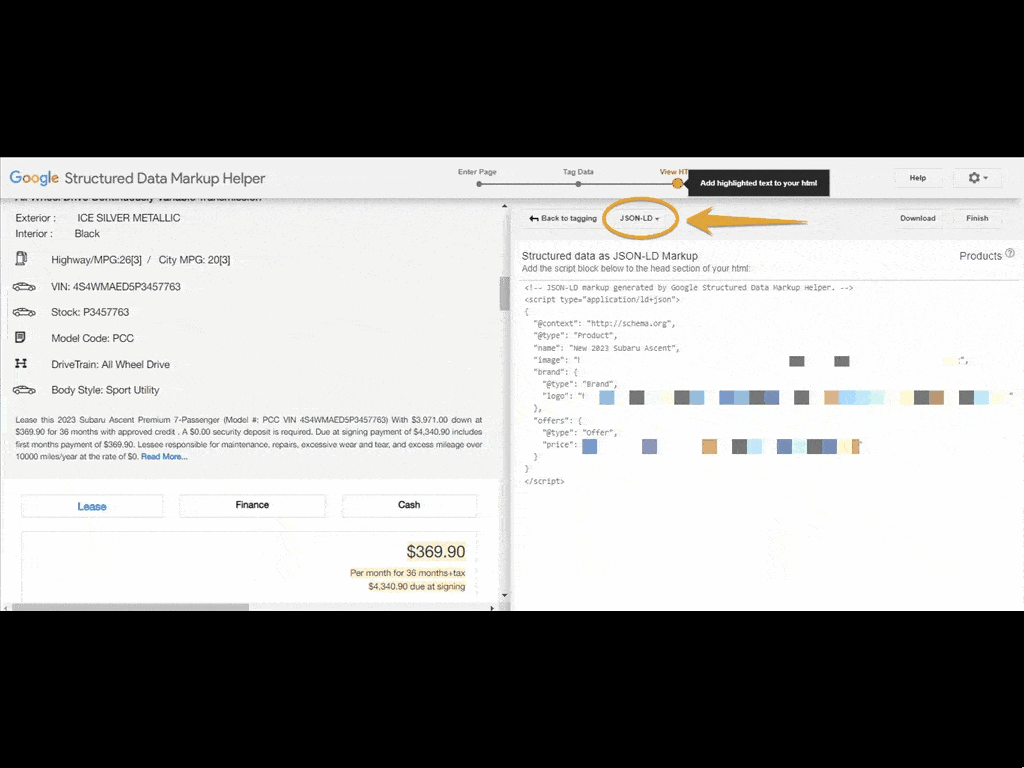
Once you’re done tagging, click the Create HTML red button at the top right corner. You’ll be given the option to download the code in either JSON-LD or microdata. It’s best practice to use JSON-LD.
5. Add your schema markup code to your site
Log onto your content management system (CMS) and add your code. If you put your HTML instead of URL in the Structured Data Markup Helper in step #2, copy and paste the HTML file, and paste it to your CMS or source code.
6. Test your schema markup
Use Google’s Structured Data Testing Tool to test your markup for any errors. Enter either your URL with the schema markup or the code snippet. The tool will show you the errors and warnings it detects.
You can directly edit the code on the Structured Data Testing Tool to fix any errors. Click the Run Test button to check your changes.
Schema markup best practices
Now that you know how to add schema markup on your pages, here are best practices to take note of to maximize its benefits:
- Use the JSON-LD format. While Google supports JSON-LD, Microdata, and RDFa formats, JSON-LD Is the easiest format to maintain.
- Find the most common and suited schema markup for your business. Improve your pages’ click-through rates by using schema markup that will help your target audience and address their search intent.
- Mark up what is on the page. Provide your target audience with the content they expect when they click on the rich result that features your page. For example, your product page’s structured data has the pricing and special offer information. Ensure that the product page has these details, too.
- Always test your structured data. Ensure your page has no schema markup issues by always testing it.
Start using schema markup on your website today!
Schema markup enriches how your pages appear in SERPs. It provides a great search experience for your target audience and can increase your pages’ click-through rates.
Let’s Drive Results Together 
Table of Contents
- What is Schema Markup?
- Why is Schema Markup Important for Search Engine Optimization (SEO)?
- Types of Schema Markup
- How to Add Schema Markup for Your Pages
- 1. Visit Google’s Structured Data Markup Helper
- 2. Select a Page from Your Site That You’ll Mark Up
- 3. Mark Up the Different Elements on Your Page
- 4. Generate the HTML Code
- 5. Add Your Schema Markup Code to Your Site
- 6. Test Your Schema Markup
- Schema Markup Best Practices
- Start Using Schema Markup on Your Website Today!
Let’s Drive Results Together 
Writers

Related Resources
- What Are Sitemaps (And Why Use Sitemaps for SEO)?
- What Happens if You’re the Target of an SEO Attack?
- What is a Robots.txt File and Why is It Important?
- What is Page Speed SEO, and How Can You Optimize for It?
- What is Website Security and How Can You Optimize for It?
- Why is Flash Bad for SEO? 6 Reasons to Avoid Flash for SEO
- Why is My Website Slow? 10 Reasons for Slow-Loading Websites
- 9 Website Accessibility Best Practices You Can Emulate
- Absolute vs. Relative URLs in SEO: Which Should You Use?
- How to Add Schema Markup for SEO (And Improve Your SEO)